As a leading orthopaedic clinic in Raleigh and Cary, we get all types of questions from patients about bone and joint conditions. In this article, our ortho experts answer some of the most common orthopedic questions.
1. What is orthopaedic medicine?
Orthopaedic medicine is a specialty focusing on the diagnosis, correction, prevention and treatment of injuries or disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic doctors address conditions related to the bones, joints, muscles, ligaments and tendons in the body.
2. How can I avoid orthopaedic issues?
As the body’s support system, bones need to stay healthy and strong. Regular exercise is important to maintain bone health. Exercise will also help you avoid orthopaedic issues in the future. Diet and nutrition are also critical to orthopaedic health. A regular intake of calcium and vitamin D in your diet will contribute to strong, healthy bones. Minimizing caffeine and alcohol consumption supports healthy bones and joints, as does avoiding smoking.
3. What is osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is inflammation of the joints where two or more bones are connected. Cartilage, the connective tissue in our joints, protects the joints by absorbing pressure and shock when we move. Arthritis can occur when cartilage erodes, causing weak, stiff or painful joints. There are over 100 different types of arthritis; the two most common types are osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Orthopedic doctors can help relieve pain related to osteoarthritis.
4. What causes arthritis?
Injury, wear and tear, hereditary factors, metabolic abnormalities, infections and autoimmune disorders are among the many causes of arthritis. Generally, OA is caused by normal wear and tear of the joints, while RA is an autoimmune disorder that occurs when your body’s immune system attacks the tissues of the body.
5. Why do I have shoulder pain?
Shoulder pain is another common orthopaedic condition. The source of pain is often a torn rotator cuff. The two leading causes of rotator cuff tears are degeneration and injury. Continued use after a tear can cause further damage to your rotator cuff. Patients experiencing chronic shoulder or arm pain should see an orthopaedic shoulder specialist. An orthopaedic doctor typically starts with a non-surgical treatment to address shoulder pain. Steroid injections and/or physical therapy will often ease the pain and improve function in the shoulder without the need for surgery.
6. When should I use ice for an injury?
Ice should generally be used within the first 24 to 48 hours after an injury to reduce pain and swelling. Follow the PRICE protocol: Protection, Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation. Do not use ice directly on the skin. Depending on the area of the injury, ice should be used for 10 to 20 minutes. The thicker the tissue of the injured area, the longer the application time. Knee injuries typically require 15 minutes of icing, while the quadriceps and hamstrings require 20 minutes. Thinner tissue, such as ankles and feet, requires only 10 minutes.
7. When should I use heat for an injury?
Heat is helpful for muscle pain and stiffness. Applying direct heat, such as a heating pad, for 15 to 20 minutes can relieve minor tension or stiffness. Longer periods of direct heat, such as a warm bath, can help alleviate moderate to severe pain. Heat can also be used to warm up the muscles before physical activity. Do not apply heat when swelling or inflammation is present.
8. What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
Patients experiencing numbness, tingling and weakness in their hands, wrists and occasionally arms may have carpal tunnel syndrome. This condition is caused by a compressed nerve in the carpal tunnel, a narrow passageway on the palm side of the wrist. Carpal tunnel can worsen over time, so be sure to visit an orthopaedic hand specialist soon after symptoms occur.
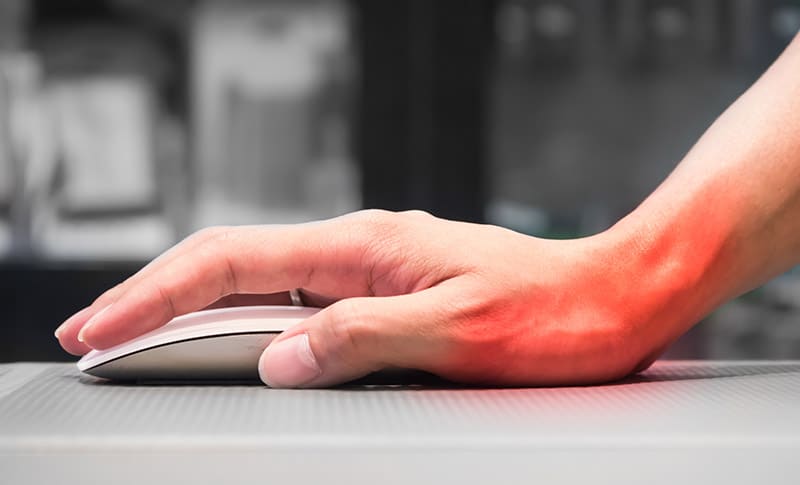

9. What causes carpal tunnel?
There is often no single cause of carpal tunnel syndrome. However, several risk factors may contribute to this condition. Continuous pressure on the nerves as a result of obesity or repetitive motion can be significant risk factors for carpal tunnel. Inflammatory conditions can also play a role. Using a wrist splint or limiting certain activities may help relieve symptoms of carpal tunnel.
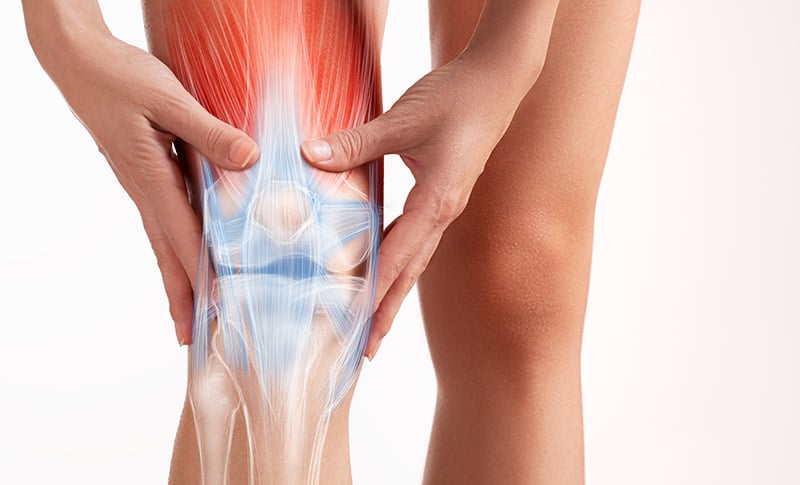
10. What causes knee pain?
Knee pain is one of the most common orthopaedic issues affecting people of all ages. Knee pain is typically the result of injury or inflammation. The knee is one of the joints most prone to injury, which may result in acute pain. Osteoarthritis and other inflammatory diseases may cause chronic knee pain. A board-certified orthopaedic knee specialist may recommend steroid injections, a knee brace or physical therapy, which can often relieve symptoms of knee pain. Some cases may require more aggressive treatment, such as surgery to correct a mechanical breakdown of the knee.
Ask us your orthopaedic questions
If you have questions related to your bone and joint health, our fellowship-trained orthopaedics specialists are available for a consultation. Our goal is to address your sports injury, workplace injury or degenerative condition with the best orthopedic care available in the region. Contact Cary Ortho today to schedule an appointment at one of our convenient locations.